Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-032, 159 Pages, 2024/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2022, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near- field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-019, 70 Pages, 2023/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2023, we continue R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. In the "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", we conduct the coupled analysis on the full-scale engineered barrier system performance experiment and test the coupled simulation code through comparison with different simulation codes in the international DECOVALEX-2023 collaboration project. Borehole investigations are also carried out for solute transport experiments in the Koetoi Formation. As for "Demonstration of repository design concept", we carry out in situ experiments and data analysis on concrete deterioration under the subsurface conditions. Geophysical surveys are also carried out around an experimental tunnel to be newly excavated at the 350m gallery and characterise the initial conditions of the excavation damaged zone. For the "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations", we analyse the results of the hydraulic disturbance tests conducted in previous years and understand the relationship between rock stress / stress state and fault / fracture hydraulic connectivity. Concerning the construction and maintenance of the subsurface facilities, the 350 m gallery is extended and shafts are sank to a depth of 500 m.
Minari, Eriko*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.793 - 803, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Shima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Seiji
MRS Advances (Internet), 8(6), p.243 - 249, 2023/06
In the intermediate depth disposal of relatively high-level radioactive waste, a method to confirm whether the borehole for monitoring is properly sealed should be developed in advance. In this study, groundwater flow analyses were performed for the hydrogeological structures with backfilled boreholes, assuming sedimentary rock area, to understand what backfill design conditions could prevent significant water pathways in the borehole, and to identify the confirmation points of borehole sealing. The results indicated the conditions to prevent water pathways in the borehole and BDZ (Borehole Disturbed Zone), such as designing the permeability of bentonite material less than or equal to that of the host rock, and grouting BDZ.
Sakai, Akihiro
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (64), p.24 - 33, 2023/05
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has proceeded with the project of near surface disposal of radioactive waste generated from research facilities, etc. as the implementing body. On the other hand, Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has established the safety regulations and standards for the operation of the disposal facilities. This report outlines the disposal project of JAEA and the development of the regulations and standards for the disposal by NRA.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2022-026, 66 Pages, 2022/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2022, we continue to conduct research on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations", which are the important issues shown in the Horonobe underground research plan from fiscal year 2020. The main studies to be conducted in fiscal year 2022 are as follows. As "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", we will continue to the test under the simulated condition in which the heat generation by the high-level radioactive waste has subsides in the full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment. We will also conduct solute transport experiment with model testing that take into account the effects of organic matter, microbes, and colloids, and initiate borehole investigation to evaluate solute transport experiments on fractures distribute in Koetoi formation. As "Demonstration of repository design concept", we will continue experiment and analysis of concrete deterioration in the underground environment as a demonstration of remote technique for emplacement and retrievable. As a demonstration of the closure techniques, laboratory tests will be continued to investigate the mechanism of bentonite runoff behaviour, which could be a factor in changing the performance of backfill material, and to expand data on swelling and deformation behaviour. In addition, in-situ borehole closure tests will be conducted to evaluate the applicability of the closure method. As "Understanding of buffering behaviour of
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2022-025, 164 Pages, 2022/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2021, we continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2021-053, 133 Pages, 2022/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2020, JAEA continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on nearfield system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, 'full scale engineered barrier system (EBS) experiment' and 'solute transport experiment' were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". 'Development and testing of EBS emplacement / retrieval and tunnel closure technologies' and 'evaluation of EBS behavior over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, 'evaluation of hydromechanical responses of faults to water pressure changes' and 'development of techniques for evaluating self-sealing behavior of an excavation damaged zone after backfilling'. The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, JAEA will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, 'evaluation of hydromechanical responses of faults to water pressure changes' and 'development of techniques for evaluating self-sealing behavior of an excavation damaged zone after backfilling'. The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, JAEA will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Ochs, M.*; Dolder, F.*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 136, p.105161_1 - 105161_11, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:66.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Various types of radioactive wastes and environments contain organic substances that can stabilize the aqueous complexes with radionuclides and therefore lead to a decrease of sorption. The present study focuses on testing a methodology to quantify sorption reduction factors (SRFs) in the presence of organic ligands for cement systems. Three approaches for the estimation of SRFs; (1) analogy with solubility enhancement factors, (2) radionuclide speciation based on the thermodynamic calculations, and (3) experimental sorption data in ternary systems, were coupled and tested for the representative organic ligands (ISA and EDTA) and selected key radionuclides (actinides). Our approach allows to critically evaluate the dependence of SRFs for various systems on the chosen method of quantification, in accordance with the data availability for a given systems. The reliable SRFs can only be derived from the sorption measurements in ternary systems. SRF often need to be derived in the absence of such direct evidence, and estimations need to be made based on analogies and speciation information. However, such estimates may be subject to substantial uncertainties.
Park, Y.-J.*; Sawada, Atsushi; Ozutsumi, Takenori*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Morita, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Discrete Fracture Network Engineering (DFNE 2022) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
Safety analysis for underground disposal facilities for high-level radioactive waste requires thorough understanding of long-term groundwater flow and nuclide migration processes in geologic media. In the coastal subsurface systems, groundwater flow is defined by the complex interactions between freshwater of meteoric origin and denser saline water from the sea. In addition, sea levels are expected to fluctuate significantly due to a transgression and regression of the sea over the millions of years for safety analysis. This study presents long-term evolution of groundwater environment such as salinity concentration and flow velocity with focus of the interaction between fractures and matrix blocks in regional and near-field scale analysis framework for groundwater flow and nuclide migration for underground disposal facilities in hypothetical fractured crystalline coastal systems.
Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Saito, Tatsuo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(8), p.610 - 614, 2021/08
, 63(8), p.610 - 614, 2021/08
Regarding the handling of uranium bearing waste, which is contaminated with uranium, which is a naturally occurring radionuclide, and its descendant nuclides, in recent years, the Japan Nuclear Regulatory Commission, etc. have been carefully and actively deliberated based on the knowledge of natural science and safety engineering. It was carried out, and as of March 2021, a certain policy has been shown. On the other hand, when disposing of uranium waste, which may cause dose exposure to future generations, the authors consider not only the science and engineering perspectives that have been conducted so far, but also the humanities and social science perspectives. We have been discussing with experts in related fields, thinking that it is necessary. In this report, we will introduce the background that brought about such an idea and the direction of future discussions.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2021-009, 54 Pages, 2021/07
The Horonobe URL Project is being pursued by the JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In 2021 fiscal year (2021/2022), JAEA continue to conduct research on "Demonstration of EBS in geological environment", "Demonstration of disposal concept", and "Validation of buffer capacity of the sedimentary rock to tectonism", which are the important issues shown in the Horonobe underground research plan after 2020 fiscal year. The main studies to be conducted in 2021 fiscal year are as follows. As "Demonstration of EBS in geological environment", we will shift to the test under the condition that the influence of heating is eliminated in the full scale EBS experiment. As "Demonstration of disposal concept", as a demonstration of the closure techniques, it details the conditions under which long-term transitions in the tunnel and surrounding bedrock have a significant impact on safety assessments. And we will continue engineering scale experiment to confirm the workability and performance of plugs and laboratory tests to examine the interaction between backfilling materials and buffer materials. As "Validation of buffer capacity of the sedimentary rock to tectonism", we will analyze the results of the hydraulic disturbance test and continue to study the hydraulic disconnection of faults/fissures in the Wakkanai Formation. As an advancement of technology for investigating and evaluating areas where the flow of groundwater is extremely slow, a boring exploration will be conducted to confirm the three-dimensional distribution of the fossil seawater area.
Wilson, J.*; Bateman, K.; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Geochemistry, 130, p.104979_1 - 104979_19, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:59.93(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The concept of deep geological disposal will include the multiple use of cement-based materials. In the case of argillaceous host rocks, the presence of hyperalkaline cement porefluid results in the destabilization of primary minerals in the argillite, resulting in the development of a zone of alteration at cement-rock interfaces. The process understanding gained from experimental, analogue, and modelling studies has been reviewed, and remaining areas of uncertainty identified. Although there is a reasonably good understanding of the mineral assemblages that are likely to occur due to cement-rock interactions, there are still some areas where a degree of uncertainty remains, in particular: the evolution of cement-argillite interfaces at T  25
25 C; the rates at which secondary minerals form; the extent of pore clogging due to secondary mineral precipitation; the implications of alteration for radionuclide transport.
C; the rates at which secondary minerals form; the extent of pore clogging due to secondary mineral precipitation; the implications of alteration for radionuclide transport.
Kitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-020, 164 Pages, 2021/03
Part of JAEA's Thermodynamic Database (JAEA-TDB) for solubility and speciation of radionuclides (JAEA-TDB-RN) for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes has been updated with subsuming the database for geochemical calculations (JAEA-TDB-GC). This report has focused to update JAEA-TDB-RN after selecting change in standard Gibbs free energy of formation (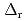
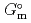 ), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (
), change in standard enthalpy change of formation (


 ), standard molar entropy (
), standard molar entropy (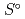
 ) and, heat capacity (
) and, heat capacity (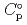 ), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (
), change in standard Gibbs free energy of reaction (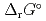
 ), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
), change in standard enthalpy change of reaction (
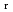


 ) and standard entropy change of reaction (
) and standard entropy change of reaction (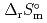 ) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
) as well as logarithm of equilibrium constant (log
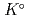 ) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
) at standard state. The extent of selection of these thermodynamic data enables to evaluate solubility and speciation of radionuclides at temperatures other than 298.15 K. Furthermore, the latest thermodynamic data for iron which have been critically reviewed, selected and compiled by the Nuclear Energy Agency within Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA) have been accepted. Most of previously selected log
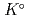 have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
have been refined to confirm internal consistency with JAEA-TDB-GC. Text files of the updated JAEA-TDB have been provided for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Kitamura, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(2), p.839 - 845, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.99(Chemistry, Analytical)Thermodynamic data for radium for radioactive waste management have been predicted using an electrostatic model and correlation with the ionic radii of the alkaline earth metals. Estimation of the standard Gibbs free energy of formation and standard molar entropy of aqueous radium species and compounds has been based on such approaches as extrapolation of the thermodynamic properties of strontium and barium, and use of a model of ion pair formation. The predicted thermodynamic data for radium have been compared with previously reported values.
Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi
JAEA-Review 2020-042, 116 Pages, 2021/01
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction Phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). This report summarizes the results of the investigations for the 2019 fiscal year (2019/2020). The investigations, which are composed of "Geoscientific research" and "R and D on geological disposal technology", were carried out according to "Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project Investigation Program for the 2019 fiscal year". The results of these investigations, along with the results which were obtained in other departments of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), are properly offered to the implementations and the safety regulations. For the sake of this, JAEA has proceeded with the project in collaboration with experts from domestic and overseas research organizations.
Kitamura, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Goto, Takahiro*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.58 - 71, 2020/12
Evaluation and estimation of solubility values are required for a performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. Selection of solubility-limiting solid phases (SSPs) that control the solubility of radionuclides is necessary for the evaluation and estimation of solubility values. The authors have developed a methodology for selection of the SSP through a calculation of saturation indices (SIs) using thermodynamic database to show a transparent procedure for the selection. Literature survey should be performed to confirm decision of the SSP from candidate SSPs which generally have larger SIs from realistic point of view for precipitation and solubility control. The authors have selected the SSPs for the elements of interest for the latest Japanese performance assessment in bentonite and cement porewaters after grouping various water compositions.
Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi
JAEA-Review 2020-022, 34 Pages, 2020/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface-based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Demonstration of EBS in geological environment", "Demonstration of disposal concept", and "Validation of buffer capacity of the sedimentary rock to tectonism" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the URL will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. JAEA summarizes the research and development activities of the important issues carried out during the 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan, and set out three important issues after 2020 fiscal year. After consultation with Hokkaido and Horonobe town, JAEA formulated the Horonobe underground research plan after 2020 fiscal year within the 3rd and 4th Mid- and Long-term Plan. This report summarizes the investigation program for the 2020 fiscal year (2020/2021).
Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake; Sato, Fuminori; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Kataoka, Shoji; Okada, Shota; Sasaki, Toshiki; Inoue, Junya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(11), p.658 - 663, 2020/11
, 62(11), p.658 - 663, 2020/11
no abstracts in English
Sugita, Yutaka; Taniguchi, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Kanamaru, Shinichiro*; Okumura, Taisei*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(3), p.121 - 135, 2020/09
A series of structural analysis of disposal containers for direct disposal of spent fuel was carried out to provide preliminary estimates of the required pressure resistance thickness of the disposal container. Disposal containers were designed to contain either 2, 3 or 4 spent fuel assemblies in linear, triangular or square arrangements, respectively. The required pressure resistance thickness was evaluated using separation distance of the housing space for each spent fuel assembly as a key model parameter to obtain the required thickness of the body and then the lid of the disposal container. This work also provides additional analytical technical knowledge, such as the validity of the setting of the stress evaluation line and the effect of the model length on the analysis. These can then be referred to and used again in the future as a basis for conducting similar evaluations under different conditions or proceeding with more detailed evaluations.